Raktamokshan
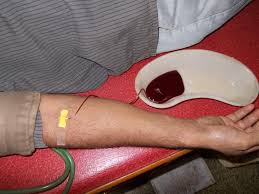
Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of medicine, has been a beacon of natural healing for centuries. Among its various therapeutic methods, Raktamokshana, or bloodletting, stands out as a unique and potent treatment. In this article, we delve into the depths of Raktamokshana, exploring its history, benefits, procedures, and its place in the modern world.
Introduction
Ayurveda, the “science of life,” encompasses a holistic approach to well-being. Raktamokshana, one of its lesser-known yet impactful therapies, involves the cleansing of the blood to promote overall health. Panchakarma is Ayurvedic detoxification treatment in Ayurveda. Out of which raktamokshana is one. It is unique way to clean and purify blood.
Understanding Ayurvedic Principles
Central to Ayurveda are the three doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha—that govern an individual’s constitution. The concept of blood purification aligns with the balance and harmony of these doshas. In Ayurvedic philosophy, impure blood is believed to be a breeding ground for diseases, making Raktamokshana pivotal in restoring this equilibrium. This impurities in blood are excessive Vata, Pitta or Kapha Dosha, Aam (Undigested nutrients) or toxins.
Types of Raktamokshana
1. Siravedha (Venesection):
- This method involves the controlled incision of veins, allowing the extraction of a specific quantity of blood. Siravedha is often used to alleviate disorders related to excess Pitta dosha, such as skin diseases, inflammation, and certain blood disorders.
2. Jalaukaavacharana (Leech Therapy):
- Leeches are applied to specific points on the body to draw out blood. Jalaukaavacharana is believed to purify the blood, improve circulation, and address conditions like varicose veins, joint pain, and skin diseases. The saliva of the leech contains bioactive compounds that contribute to the therapeutic effect.
3. Pracchana (Bloodletting with a Surgical Instrument):
- In Pracchana, a surgical instrument like a lancet or a scalpel is used to make small incisions in the affected area for bloodletting. This method is employed to treat conditions like abscesses, localized swelling, and inflammatory disorders.
4. Shringa (Horn Method):
- Shringa involves creating controlled vacuum pressure using animal horns. One end of the horn is placed on the skin, and the other end is heated. As the heated air creates a vacuum, blood is drawn out through small incisions. This method is used for conditions such as joint pain and skin disorders.
5. Alabu (Cupping):
- Cupping, known as Alabu in Ayurveda, involves the use of glass or bamboo cups to create suction on the skin. This method promotes blood circulation, reduces stagnation, and addresses musculoskeletal issues. Cupping is often employed for pain relief and detoxification.
Procedure of Raktamokshana
The procedure is conducted with precision and adherence to Ayurvedic principles. Here is an overview of the general steps involved in the Raktamokshana process:
1. Patient Assessment:
- Before initiating Raktamokshana, a thorough assessment of the patient’s overall health, medical history, and specific health concerns is conducted. This helps determine the suitability of the procedure for the individual.
2. Selection of Method:
- Ayurveda offers various methods of Raktamokshana, and the choice of method depends on the patient’s constitution, doshic imbalance, and the nature of the health issue. Common methods include Siravedha (venesection), Jalaukaavacharana (leech therapy), and Pracchana (bloodletting with a surgical instrument).
3. Preparation of the Patient:
- The patient is prepared for the procedure by ensuring they are in a calm and relaxed state. In some cases, dietary and lifestyle modifications may be recommended leading up to the Raktamokshana for optimal results.
4. Sterilization of Instruments:
- All instruments used in the procedure, whether it be lancets, or surgical instruments, are thoroughly sterilized to prevent infection and ensure a hygienic environment.
5. Application of Local Anesthesia (if necessary):
- Depending on the method chosen and the sensitivity of the area, a local anesthetic may be applied to numb the region and minimize discomfort during the procedure.
6. Bloodletting Process:
- The actual bloodletting process takes place according to the chosen method. This could involve making small incisions, applying leeches to specific points, or utilizing surgical instruments in a controlled manner.
7. Collection of Blood:
- The blood is collected in a clean and sterile container. The amount extracted is carefully measured to ensure it aligns with Ayurvedic principles and the patient’s individual health requirements.
8 Post-Procedure Care:
- After the bloodletting, the patient is given adequate time to rest. Ayurvedic post-procedure care, including dietary recommendations and lifestyle guidelines, may be provided to support the body’s recovery.
9. Monitoring and Follow-up:
- The patient’s response to Raktamokshana is monitored, and follow-up sessions may be recommended based on individual needs. Adjustments to the treatment plan are made as necessary.
Benefits of Raktamokshana
Raktamokshana, the Ayurvedic practice of controlled bloodletting, is believed to offer a range of therapeutic benefits aimed at balancing the doshas, improving circulation, and addressing specific health concerns. Here are some key benefits associated with Raktamokshana:
1. Dosha Balancing:
- Raktamokshana is considered effective in balancing the doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. By removing excess or vitiated blood, it helps restore harmony to the body’s constitutional elements.
2. Improved Blood Circulation:
- The controlled removal of blood in Raktamokshana promotes enhanced circulation. Improved blood flow contributes to the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to various tissues, supporting overall vitality.
3. Detoxification:
- Raktamokshana is believed to aid in the detoxification of the blood. By eliminating impurities and excess toxins, it contributes to a cleaner and healthier circulatory system.
4. Skin Disorders:
- The practice is often employed to address skin disorders such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Raktamokshana is thought to purify the blood, reducing the manifestation of skin conditions.
5. Inflammatory Conditions:
- Conditions characterized by inflammation, such as arthritis and gout, may benefit from Raktamokshana. The removal of inflammatory elements from the blood is believed to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation.
6. Varicose Veins:
- Raktamokshana is considered beneficial for improving venous circulation and addressing conditions like varicose veins. It helps relieve venous congestion and may support healthier blood vessel function.
7. Joint Disorders:
- Individuals with joint disorders, including stiffness and pain, may find relief through Raktamokshana. The practice is thought to enhance the circulation of synovial fluid, promoting joint health.
8. Headaches and Migraines:
- Raktamokshana is believed to alleviate certain types of headaches and migraines by promoting better blood flow to the head and reducing excess Pitta dosha.
9. Hypertension Management:
- In Ayurveda, Raktamokshana is considered in the management of hypertension. The controlled removal of blood may contribute to regulating blood pressure levels.
FAQs
- Raktamokshana is generally safe but should be done under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner. Individuals with certain medical conditions may need special consideration.
- The frequency of Raktamokshana depends on individual health needs. A qualified practitioner can determine an appropriate schedule based on specific conditions.
- While generally safe, mild side effects like bruising or swelling may occur. Serious complications are rare when the procedure is performed by a skilled professional.
-
- The timeline for results varies based on individual health conditions. Some may experience immediate benefits, while others may notice gradual improvements over weeks.
Uniqueness of our therapies
At Arogya Mandir – Shri Siddhanath Ayurvedic Hospital, Miraj, we delve deeply into the ayurvedic examination of each patient. Utilizing noninvasive Ayurvedic diagnostic tools such as Ashtavidha Parikshan and Nadi Parikshan, we precisely determine the pathogenesis of the disease and then prescribe therapies tailored to the specific condition. This approach leads to expedited results.
Our therapies boast the following distinctive features:
– Tranquil and hygienic therapy rooms staffed with trained therapists in a positive environment.
– Selection of appropriate massage oil based on the patient’s Prakruti and the condition of the disease.
– Complimentary Prakruti and Dhatu Sarata examinations before the commencement of therapies.
– Authenticated procedures for each therapy.
– Judicious use of herbal medicines and instruments during the therapy sessions.
– Specialized rooms equipped with all facilities for inpatient care.
Feel free to share this article at no cost.
Copyright message – Dr. Prashant Chivate has published this article on drchivateayurved.org for informational purposes about diseases. Any other use of this article is strictly prohibited. All rights reserved.
